| Procedure | Periodontology |
Get a special offer for your treatment now
Periodontal diseases are diseases that affect the area around teeth and are seen in supporting structures such as gums, supporting bone and periodontal connective tissue. If disease measures are not taken, it causes inflammation that irritates the gums. This infection can compromise or even destroy dental support structures. It accumulates more bacteria by creating periodontal pockets and creates convenient conditions for their reproduction. Periodontal diseases, if not treated properly, can lead to irreversible harm to health as well as tooth loss.
Studies have revealed the link between periodontal disease and systemic diseases such as heart problems, diabetes and stroke.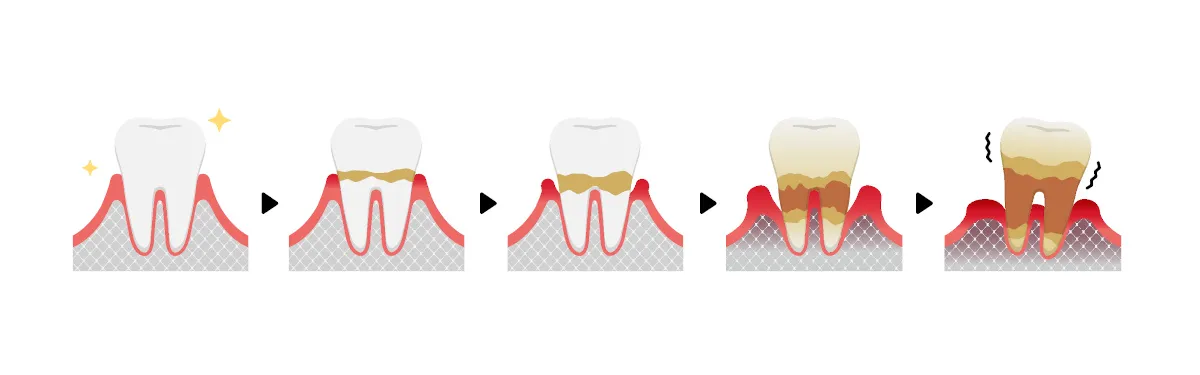
Periodontal Diseases Are Divided Into Two Groups
Without careful oral hygiene and regular consultations by the dentist, inflammation and bleeding of the gums may occur over time, even in healthy gums. These are the first stages of periodontal disease.
Periodontal disease is divided into two main groups:- 1-Gingivitis
It indicates the first stage of periodontal disease and needs to be treated immediately so that it does not progress. The main symptom is bleeding, which can occur when it is touched to gums, especially during brushing of teeth. At this stage, plaque and tartar seen on the teeth irritate the gums, which begin to show swelling and redness.
- 2-Periodontitis
It is the most critical, risky stage of periodontal diseases. Because the consequences become more severe, they begin to destroy the gums and bone tissue around the tooth. At this stage, the teeth may start to loose when it comes to the destruction of bone tissues of the teeth.
What Are The Symptoms Of Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease symptoms can be observed more aggressively in diabetics and smokers. Although in most cases the symptoms go unnoticed, in situations such as:
- Recurrent gum bleeding,
- Red gums,
- Swelling of the gums, change of shape,
- Separation of the gum from the tooth,
- Presence of pus and tartar,
- Gingival recession
During the examination, the dentist detects the presence of the disease and can assess the degree of deterioration or inflammation, including healthy-looking gums.
Causes of Periodontal Diseases
The most common cause of periodontal diseases is poor oral hygiene. There are more than 300 different types of bacteria in the mouth, many of which are potentially harmful to the gums. Bacteria living in the mouth accumulate on the surface of the teeth and in the gum groove, these are forming plaques. When bacteria reproduce above a certain level, they cause periodontal diseases.
Some risk factors for periodontal diseases include:
- Tobacco
- Diabetes
- Genetics
- Poor oral hygiene
- HIV (Aids)
Treatment of Periodontal Diseases
Treatment of periodontal diseases is a separate specialty and branch in dentistry. A periodontist or a dentist with the necessary competence can plan the required treatment to control the disease after initial evaluation. For a more effective and personalized intervention, additional complementary tests can be requested to obtain a genetic and microbiological analysis of disease-causing bacteria. This procedure can be preferred to determine which antibiotic is more suitable.
It is possible to avoid tooth extraction even at the point of Periodontitis, the more advanced stage of periodontal disease. In many cases of severe bone loss, innovative techniques can be used to restructure the lost bone and keep the teeth in the mouth healthy.
After the treatment of diseases and possible associated consequences, the stage of care begins with regular consultations. During these consultations, the dentist evaluates oral hygiene habits and helps to improve them.
Additionally, according to the clinical condition of the patient, the frequency of periodical checks is determined. Then, after treatment the periodontal disease may require additional controls according to adequate hygiene and degree of disorder.
Relationship Between Periodontal Disease and Systemic Diseases
There is a strong relationship between periodontal disease and other diseases of the body called systemic diseases; for example, cardiovascular, respiratory diseases, diabetes, birth of premature babies, emaciation and some complications in pregnancy.
The reason of this is due to the fact that microorganisms which cause periodontitis, i.e. inflammation of gum, can infect the heart, lungs and other organs through the bloodstream.
It is known that people with periodontal disease are twice as sensitive to heart disease as people with healthy gums. Another relationship that can be established is between periodontal disease and diabetes. It is known that patients with uncontrolled diabetes are more likely to develop periodontal diseases.
How To Recognize If Gums Are Healthy
Gums consist of soft tissues such as skin and cover the bones that support the teeth. These create a solid seal around the teeth and limit the area where the plaque can grow.
Healthy gums are light pink in color and rough like orange peel. They do not bleed during brushing, floss cleaning, eating and drinking. They are in regular harmony with dental contours and tightly surround the teeth.
Changes such as red or swelling gums, bleeding when brushing or flossing, and foul breath may be the first signs of gum disease.
MEDIC ANTALYA dental clinic offers services for periodontal diseases and treatments by its specialist dentists. Our clinic, which simultaneously applies international treatment methods and techniques for dental and gum diseases, is also preferred with the advantage of affordable costs.
